Humming or Grinding? Wheel Bearing Failure Signs for DTLA Drivers

Introduction
Wheel bearing noise is one of the most common—and most ignored—warning signs that your vehicle needs immediate attention. That persistent humming, grinding, or growling sound coming from your wheels isn't just annoying; it's your car telling you that critical components are failing. For Downtown LA drivers navigating everything from smooth freeways to pothole-riddled city streets, understanding wheel bearing noise and recognizing failure signs can prevent dangerous breakdowns, expensive repairs, and potential accidents.
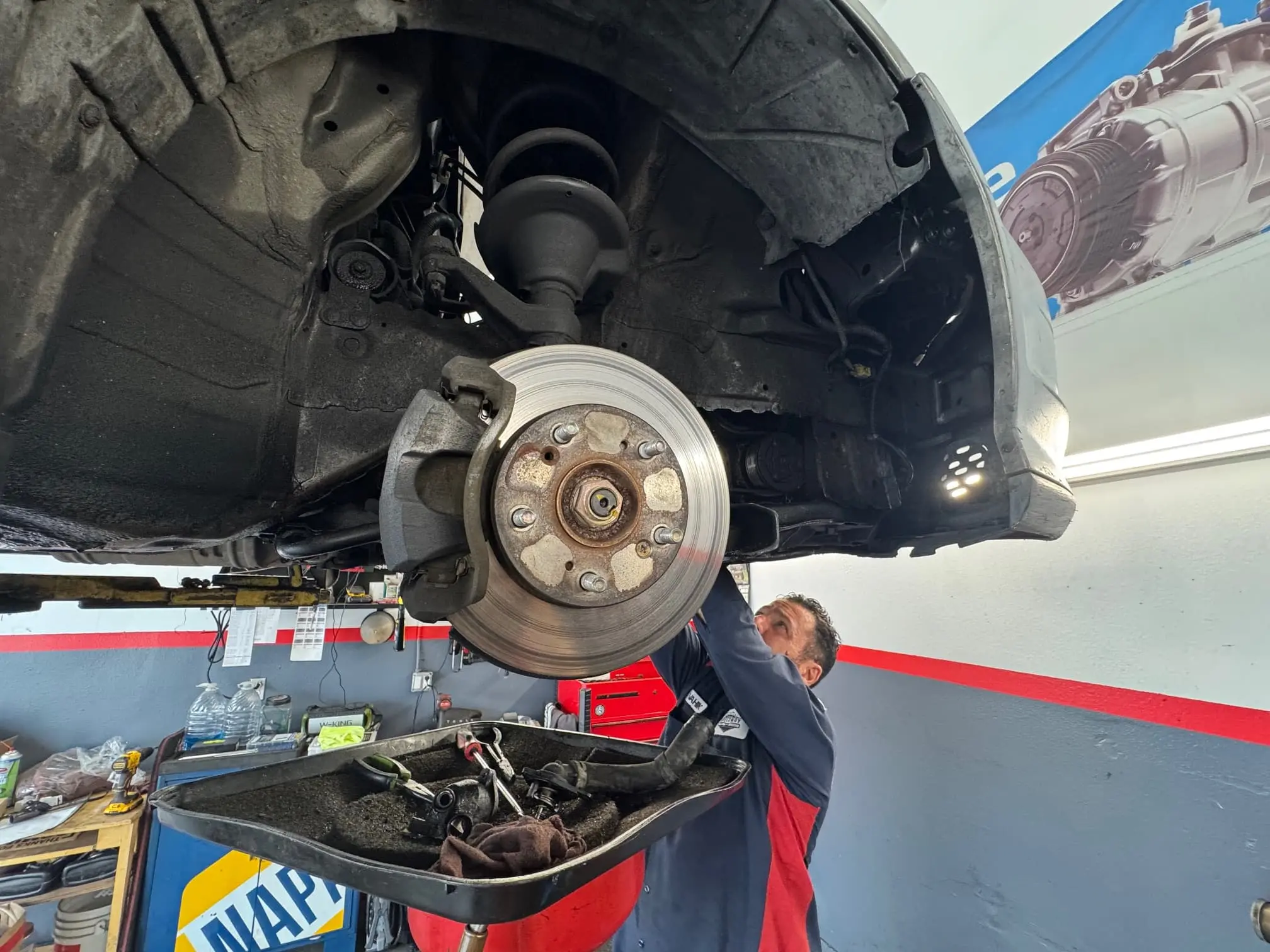
Wheel bearings are precision-engineered components that allow your wheels to rotate smoothly with minimal friction. Located in the hub assembly at each wheel, these bearings endure tremendous forces—supporting your vehicle's weight, handling lateral loads during turns, and absorbing impacts from road imperfections. When wheel bearings begin to fail, they produce distinctive sounds that change with speed and turning. Ignoring these warning signs can lead to complete bearing failure, wheel wobble, loss of vehicle control, and even wheel separation in extreme cases.
At Speedway Tire and Service, we've been diagnosing and repairing wheel bearing issues for over 25 years in Silver Lake, Echo Park, and Downtown LA. Located at 1165 West Sunset Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90012, our experienced technicians understand how LA's unique driving conditions—from stop-and-go traffic to aggressive potholes—accelerate wheel bearing wear. We provide fast, reliable wheel bearing diagnosis and replacement, getting you back on the road safely.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore wheel bearing noise including what causes it, how to identify different failure sounds, the role of hub assemblies and ABS sensors, the dangers of wheel wobble, diagnosis methods, repair costs, and when to seek professional help.
What Are Wheel Bearings and Why Do They Fail?
Understanding wheel bearings helps you recognize why failure occurs and why prompt attention is critical.
Wheel Bearing Function
Wheel bearings are precision ball or roller bearings housed in the hub assembly that allow wheels to rotate freely while supporting vehicle weight and handling lateral forces during turns. Modern vehicles typically use sealed hub bearing assemblies combining the bearing, hub, and often the ABS sensor into a single unit.
Key Functions:
•Support vehicle weight (1,000-1,500 lbs per wheel)
•Allow smooth wheel rotation with minimal friction
•Handle lateral forces during turns and lane changes
•Maintain proper wheel alignment and positioning
•Provide mounting point for brake rotors and wheels
Common Causes of Wheel Bearing Failure
Normal Wear: Wheel bearings are wear items with typical lifespans of 75,000-150,000 miles depending on driving conditions and vehicle type.
Water and Contamination: Damaged seals allow water, dirt, and road salt to enter bearings, causing corrosion and accelerated wear. LA's occasional rain combined with street washing creates contamination risks.
Impact Damage: Hitting potholes, curbs, or road debris at speed can damage bearings immediately or create cracks leading to gradual failure. Downtown LA's notorious potholes are major contributors to premature bearing failure.
Improper Installation: Incorrect installation torque, damaged seals during installation, or contamination during service causes premature failure.
Lack of Lubrication: While modern sealed bearings are pre-lubricated for life, seal damage can cause lubricant loss and rapid wear.
Overloading: Consistently carrying heavy loads or towing beyond vehicle capacity accelerates bearing wear.
Accident Damage: Collisions affecting wheels, suspension, or steering can damage bearings even without visible external damage.
According to National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) data, wheel bearing failure contributes to thousands of accidents annually, making recognition and prompt repair critical for safety.
Recognizing Wheel Bearing Noise: What You're Hearing
Wheel bearing noise produces distinctive sounds that change with vehicle speed and turning direction, helping diagnose the problem.
Humming or Droning Noise
Sound Description: Constant humming or droning sound similar to tire noise but more mechanical and persistent.
Characteristics:
•Increases with vehicle speed
•May decrease or change when turning
•Sounds like airplane or helicopter noise
•Often mistaken for tire noise initially
What It Means: Early to moderate bearing wear. The bearing's rolling elements are wearing unevenly, creating vibration and noise. This is the first warning sign—address it promptly before it progresses.
Speed Relationship: Humming typically becomes noticeable at 40-50 mph and increases proportionally with speed. It may be barely audible at low speeds but loud and intrusive at highway speeds.
Grinding or Grating Noise
Sound Description: Harsh grinding, grating, or metal-on-metal sound that's impossible to ignore.
Characteristics:
•Loud and harsh
•Clearly mechanical (not tire-related)
•May be accompanied by vibration
•Worsens rapidly
What It Means: Advanced bearing wear. The bearing's protective cage has failed, rolling elements are damaged, or the bearing is running metal-on-metal. This is a critical warning—the bearing could fail completely at any time.
Danger Level: HIGH. Grinding indicates severe damage requiring immediate attention. Continued driving risks complete bearing failure and potential wheel separation.
Growling or Rumbling Noise
Sound Description: Deep growling or rumbling sound that may come and go or change pitch.
Characteristics:
•Lower frequency than humming
•May sound like a bad tire
•Changes with speed
•Can feel like vibration through steering wheel or floorboard
What It Means: Moderate to advanced bearing wear. The bearing's internal components are damaged but not yet catastrophically failed.
Progression: Growling often progresses to grinding if ignored. Address it before it reaches the grinding stage.
Clicking or Popping Noise
Sound Description: Rhythmic clicking or popping that increases frequency with speed.
Characteristics:
•Rhythmic and speed-dependent
•May be confused with CV joint noise
•Often accompanied by wheel wobble
•Noticeable during turns
What It Means: Severe bearing damage or loose hub assembly. The bearing may have excessive play, or the hub assembly may be loose on the spindle.
Danger Level: CRITICAL. Clicking combined with wheel wobble indicates imminent failure. Stop driving and seek immediate repair.
Squealing or Screeching Noise
Sound Description: High-pitched squealing or screeching, especially during turns.
Characteristics:
•High-pitched and piercing
•Often occurs during turns
•May be intermittent
•Can be confused with brake noise
What It Means: Bearing seal failure or advanced wear. The protective seal has failed, allowing contamination and lubricant loss.
Note: Squealing can also indicate brake issues. Professional diagnosis is essential to identify the source.
The Turn Test: Diagnosing Which Wheel Has a Bad Bearing
One of the most reliable methods for identifying which wheel has a failing bearing is the turn test, which uses weight transfer during turns to isolate the problem.
How the Turn Test Works
When you turn, your vehicle's weight shifts to the outside wheels. This weight transfer loads the outside bearing more heavily while unloading the inside bearing. A failing bearing will change its noise level based on this loading.
Right Turn Test:
•Turn right (weight shifts to left wheels)
•If noise decreases or disappears: Right-side bearing is likely failing (unloaded during right turn)
•If noise increases: Left-side bearing is likely failing (loaded during right turn)
Left Turn Test:
•Turn left (weight shifts to right wheels)
•If noise decreases or disappears: Left-side bearing is likely failing (unloaded during left turn)
•If noise increases: Right-side bearing is likely failing (loaded during left turn)
Performing the Turn Test Safely
Location: Find a safe, empty parking lot or quiet street where you can make turns at 15-25 mph without traffic.
Procedure:
1.Drive straight at 15-25 mph and note the baseline noise level
2.Make a gentle right turn and listen for changes in noise
3.Return to straight driving
4.Make a gentle left turn and listen for changes in noise
5.Repeat several times to confirm the pattern
What to Listen For:
•Noise that decreases during one turn direction and increases during the other
•Consistent pattern across multiple tests
•Changes in pitch or volume, not just loudness
Limitations: The turn test works best for front wheel bearings. Rear bearing noise may be less affected by turns. If the pattern is unclear, professional diagnosis is recommended.
Front vs. Rear Bearing Noise
Front Wheel Bearings:
•Noise often felt through steering wheel
•More affected by turns (weight transfer more pronounced)
•May cause steering wheel vibration
•Easier to diagnose with turn test
Rear Wheel Bearings:
•Noise felt through seat or floor
•Less affected by turns
•May cause vehicle wandering or instability
•Harder to isolate with turn test alone
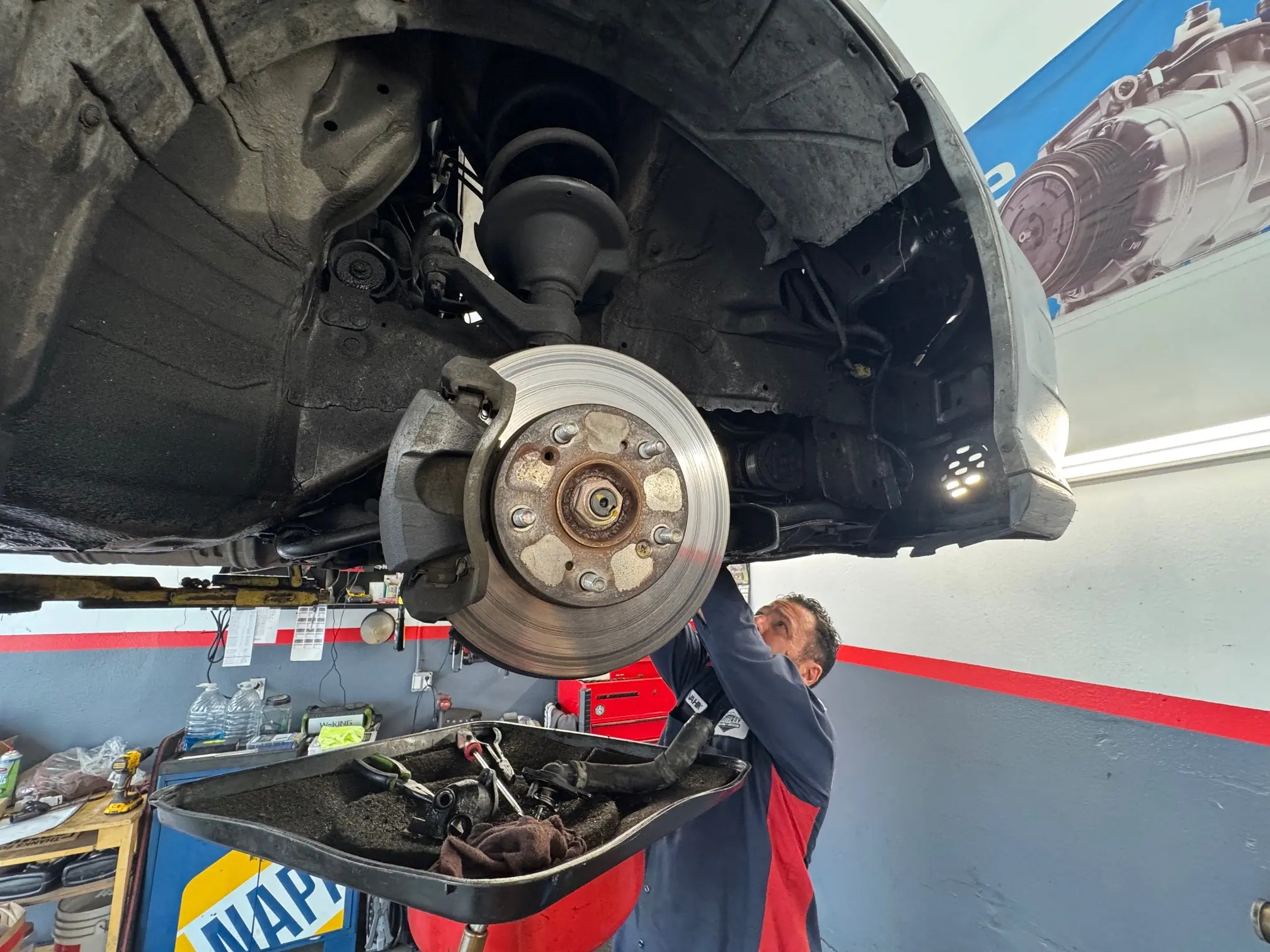
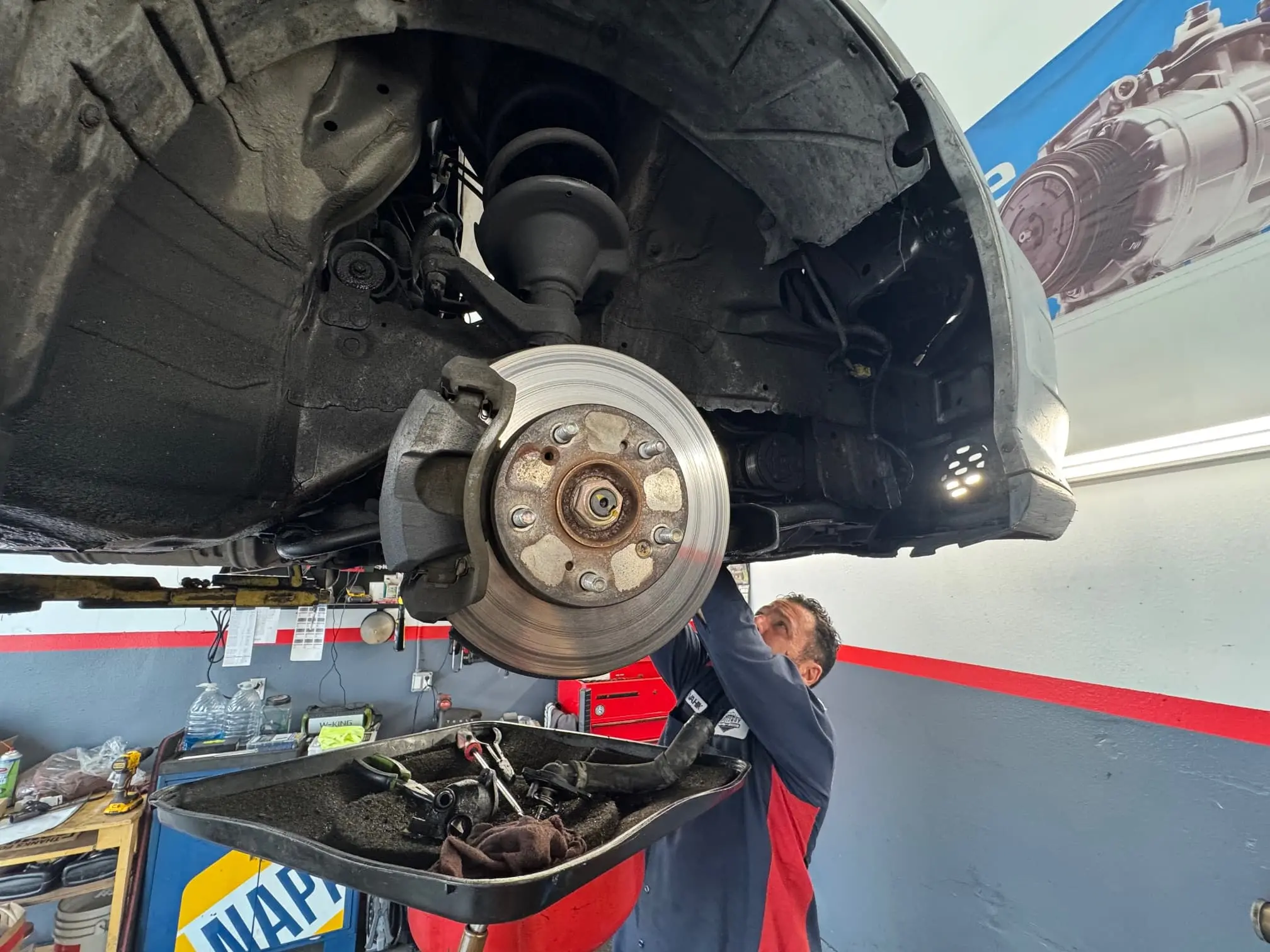
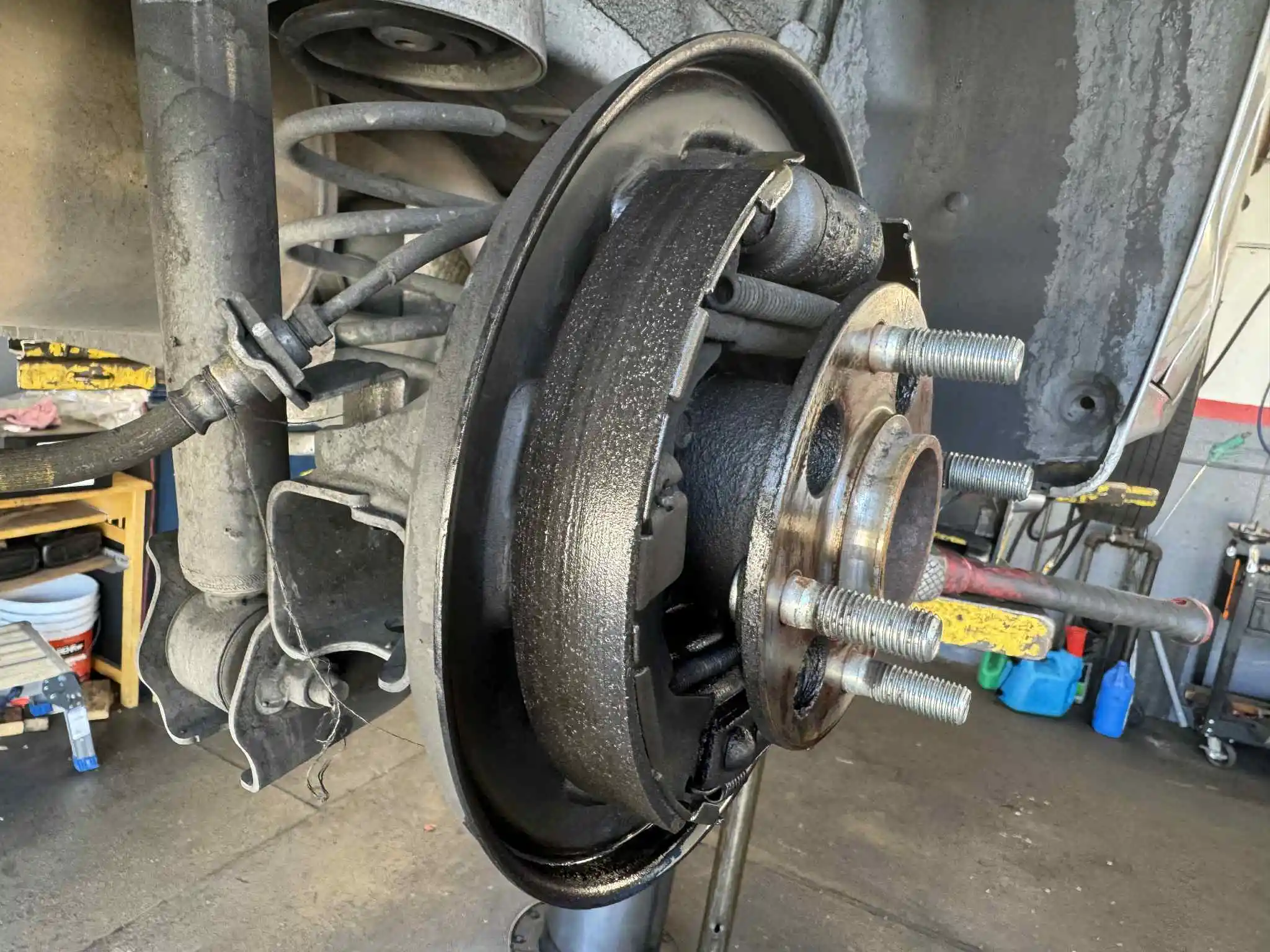
Hub Assembly: The Modern Wheel Bearing System
Modern vehicles use integrated hub assemblies that combine multiple components into a single replaceable unit, affecting diagnosis and repair.
What Is a Hub Assembly?
A hub assembly (also called a hub bearing assembly or wheel hub unit) is a pre-assembled, sealed unit containing:
•Wheel bearing (ball or roller type)
•Hub (mounting point for brake rotor and wheel)
•Mounting flange (attaches to steering knuckle or axle)
•ABS sensor ring (for anti-lock brake system)
•Seals (protect bearing from contamination)
Advantages of Hub Assemblies:
•Sealed for life (no maintenance required)
•Easier and faster to replace
•Consistent quality and tolerances
•Integrated ABS sensor ring
•Reduced installation errors
Disadvantages:
•More expensive than traditional serviceable bearings
•Entire assembly must be replaced (can't service individual components)
•Requires proper torque specifications (critical for bearing life)
Hub Assembly Failure Modes
Bearing Wear: The most common failure—the internal bearing wears out, producing noise and eventually play.
Seal Failure: Damaged seals allow water and contaminants to enter, accelerating wear and causing premature failure.
ABS Sensor Ring Damage: The integrated ABS sensor ring can be damaged by road debris, corrosion, or impact, causing ABS warning lights even if the bearing is still functional.
Mounting Flange Damage: Impact damage or improper installation can damage the mounting flange, causing looseness or improper alignment.
Bolt Failure: The bolts securing the hub assembly to the knuckle can loosen or break, causing clicking noises and dangerous wheel wobble.
Hub Assembly Replacement Considerations
Torque Specifications: Hub assembly mounting bolts and axle nuts require precise torque. Over-tightening can damage bearings; under-tightening causes looseness and premature failure.
Seal Protection: During installation, seals must not be damaged. Even minor seal damage allows contamination and causes rapid failure.
ABS Sensor Gap: The ABS sensor must be properly positioned relative to the sensor ring. Incorrect gap causes ABS malfunctions.
Brake Rotor Runout: When replacing hub assemblies, brake rotor runout (wobble) should be checked and corrected to prevent vibration and uneven brake wear.
Wheel Bearing Torque: The axle nut torque is critical. Most vehicles require 150-200 ft-lbs, but specifications vary. Always follow manufacturer specifications.
ABS Sensor and Wheel Bearing Relationship
The ABS (Anti-lock Brake System) sensor and wheel bearings are closely related in modern vehicles, and bearing failure often affects ABS function.
How ABS Sensors Work with Wheel Bearings
Modern hub assemblies integrate the ABS sensor ring (also called a tone ring or reluctor ring) directly into the bearing assembly. This toothed ring rotates with the wheel, and a magnetic sensor reads the teeth passing by, determining wheel speed.
ABS Sensor Components:
•Sensor Ring: Toothed metal ring integrated into hub assembly
•Magnetic Sensor: Stationary sensor mounted on knuckle or backing plate
•Air Gap: Small gap (0.5-2mm) between sensor and ring
•Wiring: Connects sensor to ABS control module
How It Works: As the wheel rotates, the sensor ring's teeth pass the magnetic sensor, creating a pulsing signal. The ABS control module reads this signal to determine wheel speed. If one wheel slows suddenly (indicating potential lockup), the ABS system modulates brake pressure to prevent skidding.
Wheel Bearing Failure and ABS Warning Lights
Failing wheel bearings commonly trigger ABS warning lights through several mechanisms:
Excessive Play: Worn bearings develop play (looseness), causing the sensor ring to move away from the sensor. This increases the air gap beyond specifications, weakening or interrupting the signal.
Sensor Ring Damage: Corrosion, impact damage, or debris can damage the sensor ring teeth, causing irregular or missing signals.
Sensor Ring Misalignment: Bearing wear can cause the sensor ring to wobble or tilt, creating an inconsistent air gap and erratic signals.
Magnetic Debris: Failed bearings generate metal particles that can accumulate on the magnetic sensor, interfering with signal reading.
Electrical Damage: Water intrusion through failed bearing seals can damage the sensor or wiring, causing electrical faults.
Symptoms of ABS Issues from Bearing Failure:
•ABS warning light illuminated on dashboard
•Intermittent ABS light (comes and goes)
•ABS activates unnecessarily during normal braking
•Loss of ABS function (brakes work but ABS doesn't activate)
•Traction control warning light (uses same wheel speed sensors)
Diagnosing ABS Sensor vs. Bearing Problems
Scan Tool Diagnosis: A professional scan tool can read ABS fault codes identifying which wheel sensor is malfunctioning. Common codes include:
•C0035-C0038: Wheel speed sensor circuit faults
•C0040-C0043: Wheel speed sensor signal missing or erratic
•C0050-C0053: Rear wheel speed sensor faults
Visual Inspection: Inspect the sensor ring for damage, corrosion, or debris. Check the sensor for damage, proper mounting, and clean connections.
Air Gap Measurement: Use a feeler gauge to measure the air gap between sensor and ring. Typical specifications are 0.5-2mm. Excessive gap indicates bearing play.
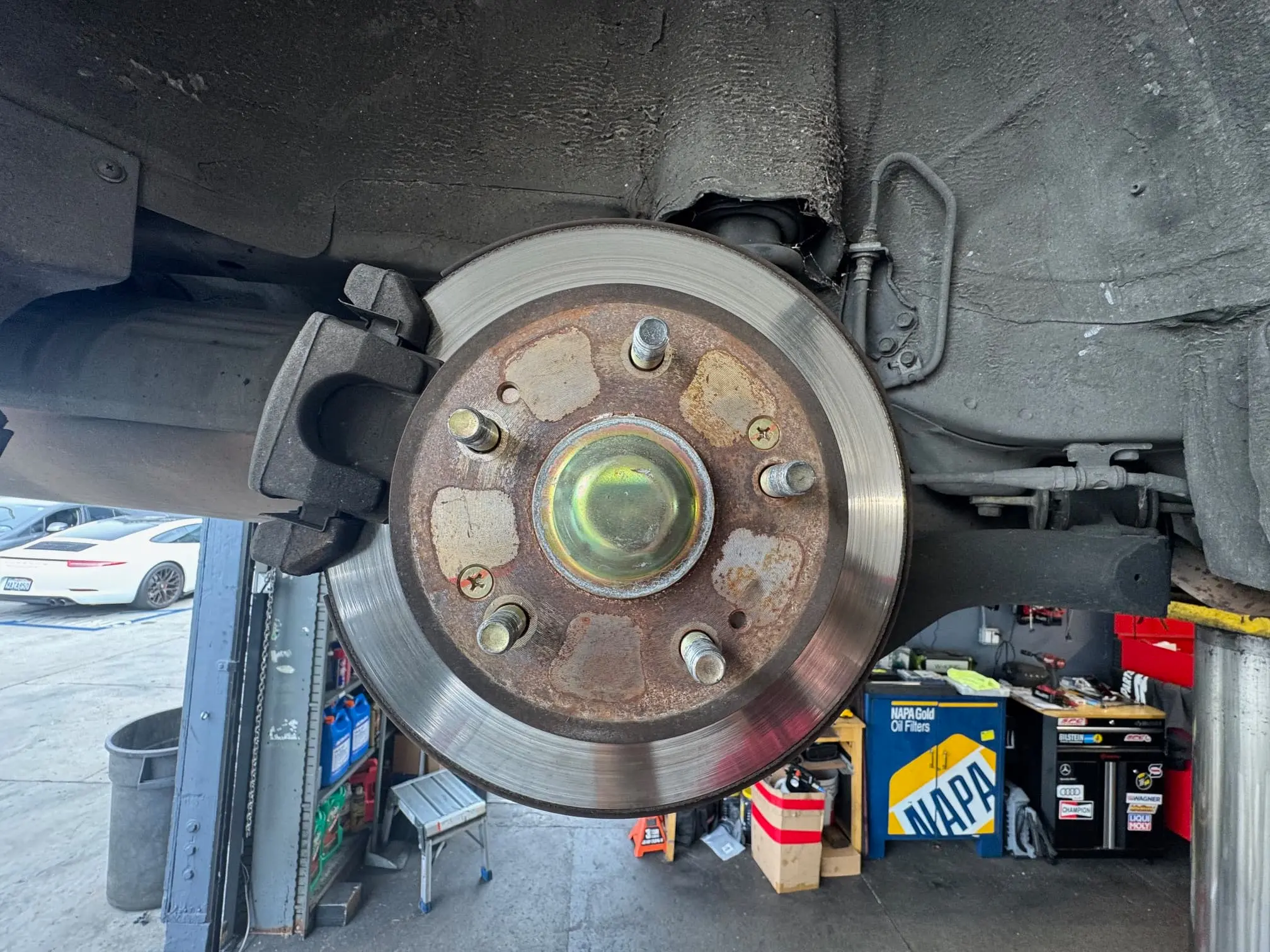
Wheel Bearing Play Test: Jack up the vehicle and check for wheel play by pushing/pulling at 12 and 6 o'clock positions. Any noticeable play indicates bearing failure.
Signal Testing: Using an oscilloscope or scan tool, observe the wheel speed sensor signal while rotating the wheel. Irregular, missing, or weak signals indicate sensor ring or bearing problems.
At Speedway Tire and Service, we use professional diagnostic equipment to accurately identify whether ABS warning lights are caused by sensor issues, bearing failure, or other problems, ensuring correct repairs the first time.
Wheel Wobble: The Dangerous Consequence of Bearing Failure
Wheel wobble is one of the most dangerous symptoms of wheel bearing failure, indicating severe wear or damage requiring immediate attention.
What Is Wheel Wobble?
Wheel wobble is excessive play or movement in the wheel assembly, causing the wheel to move side-to-side or in-and-out relative to the vehicle. This play results from worn bearings that can no longer maintain proper wheel positioning.
Types of Wheel Wobble:
•Lateral Play: Side-to-side movement (most common with bearing failure)
•Radial Play: In-and-out movement (less common, indicates severe wear)
•Combined Play: Both lateral and radial movement (critical failure)
Symptoms of Wheel Wobble
Steering Wheel Shake: Vibration or shaking in the steering wheel, especially at highway speeds or during braking.
Vehicle Wandering: The vehicle pulls or wanders to one side, requiring constant steering correction.
Uneven Tire Wear: Excessive or uneven tire wear on the affected wheel, particularly feathering or cupping patterns.
Clunking Sounds: Clunking or knocking sounds when hitting bumps or during turns.
Visible Wheel Movement: In severe cases, visible wheel movement when the vehicle is jacked up and the wheel is pushed/pulled.
Brake Pulsation: Pulsating brake pedal during braking, caused by the wobbling rotor.
Dangers of Driving with Wheel Wobble
Loss of Control: Wheel wobble affects steering response and vehicle stability, increasing accident risk, especially during emergency maneuvers.
Brake Failure: Wobbling wheels cause uneven brake pad contact, reducing braking effectiveness and potentially causing brake failure.
Suspension Damage: Excessive play damages other suspension components including ball joints, tie rod ends, and control arm bushings.
Tire Blowout: Uneven tire wear from wobbling can cause tire failure, especially at highway speeds.
Complete Bearing Failure: Continued driving with wheel wobble accelerates bearing destruction, potentially causing complete failure and wheel separation.
Wheel Separation: In extreme cases, completely failed bearings can allow the wheel to separate from the vehicle while driving—a catastrophic failure causing loss of control and potential rollovers.
Checking for Wheel Wobble
Jack Test:
1.Safely jack up the vehicle and secure with jack stands
2.Grasp the wheel at 12 and 6 o'clock positions
3.Push/pull vigorously and feel for play
4.Repeat at 3 and 9 o'clock positions
5.Any noticeable play indicates bearing failure
Specifications: Most vehicles should have zero perceptible play. Any play felt by hand indicates bearing wear requiring replacement.
Safety Note: If you detect wheel wobble, avoid driving except to reach a repair facility. If wobble is severe, have the vehicle towed.
Professional Diagnosis: What to Expect at Speedway Tire and Service
Professional wheel bearing diagnosis ensures accurate identification of problems and appropriate repairs.
Diagnostic Process
Customer Interview: We start by asking about symptoms—when the noise occurs, what it sounds like, whether it changes with speed or turns, and how long it's been present.
Test Drive: Our technicians test drive your vehicle to experience the noise firsthand, perform turn tests, and note speed-related changes.
Lift Inspection: We lift the vehicle and perform hands-on inspection:
•Check for wheel play (bearing looseness)
•Rotate wheels by hand listening for grinding or roughness
•Inspect tires for uneven wear patterns
•Check suspension components for damage
•Inspect brake components
ABS Scan: We scan the ABS system for fault codes indicating sensor or bearing issues.
Final Verification: We verify which wheel(s) have failing bearings and provide a detailed explanation and estimate.
What We Check Beyond the Bearing
Wheel bearing problems often accompany or cause other issues. Our comprehensive inspection includes:
Suspension Components: Ball joints, tie rod ends, control arm bushings, and struts—bearing play can damage these components.
Brake System: Rotors, pads, and calipers—wobbling wheels cause uneven brake wear.
Tires: Tread depth, wear patterns, and damage—bearing failure causes abnormal tire wear.
CV Axles (front-wheel drive): CV joints and boots—bearing noise can be confused with CV joint noise.
Wheel Studs and Lug Nuts: Proper torque and condition—loose wheels can mimic bearing symptoms.
This comprehensive approach ensures we identify all related issues, preventing comebacks and ensuring your safety.
Wheel Bearing Replacement: What's Involved
Understanding the replacement process helps you appreciate the work involved and why professional service is recommended.
Replacement Procedure
Vehicle Lift and Wheel Removal: The vehicle is lifted, secured on jack stands, and the wheel is removed.
Brake Caliper and Rotor Removal: The brake caliper is removed and secured (not hanging by the brake hose), and the rotor is removed from the hub.
Hub Assembly Removal:
•Front-wheel drive: The axle nut is removed, the axle is separated from the hub, and the hub assembly bolts are removed
•Rear-wheel drive: The hub assembly bolts are removed (no axle separation needed)
ABS Sensor Disconnection: The ABS sensor connector is disconnected, and the sensor wire is carefully routed out of the way.
Hub Assembly Installation: The new hub assembly is installed with new bolts (torqued to specifications), the ABS sensor is connected, and the sensor gap is verified.
Brake Rotor and Caliper Installation: The rotor is installed (cleaned and checked for runout), and the caliper is reinstalled with proper torque.
Axle Nut Installation (front-wheel drive): The axle nut is installed and torqued to specifications (typically 150-200 ft-lbs).
Wheel Installation: The wheel is installed with lug nuts torqued to specifications (typically 80-100 ft-lbs).
Final Checks: The vehicle is lowered, a test drive is performed, and ABS function is verified.
Why Professional Installation Matters
Torque Specifications: Improper torque on hub bolts or axle nuts causes premature failure. Professional technicians use calibrated torque wrenches and follow manufacturer specifications.
Seal Protection: Damaging seals during installation causes rapid failure. Experienced technicians know how to handle components without seal damage.
ABS Sensor Handling: ABS sensors are fragile and expensive. Proper handling prevents damage.
Brake Rotor Runout: Checking and correcting rotor runout prevents vibration and uneven brake wear.
Suspension Inspection: Professional technicians identify related damage requiring attention.
Proper Tools: Specialized tools (hub pullers, torque wrenches, scan tools) ensure correct installation and verification.
Wheel Bearing Replacement Costs
Understanding costs helps you budget for necessary repairs and recognize fair pricing.
Labor:
•Front Wheel Bearing: 1.5-3 hours labor
•Rear Wheel Bearing: 1-2 hours labor
Cost Factors
Vehicle Type: Luxury vehicles, trucks, and SUVs typically have more expensive parts and require more labor.
Front vs. Rear: Front bearings (especially on front-wheel drive) require more labor due to axle removal.
Two-Wheel Drive vs. Four-Wheel Drive: 4WD vehicles often have more complex hub assemblies and higher costs.
Additional Repairs: If bearing failure damaged other components (rotors, suspension parts), costs increase.
OEM vs. Aftermarket: OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts cost more but offer guaranteed fit and quality. Quality aftermarket parts (Timken, SKF, Moog) offer good value.
Should You Replace Both Sides?
Recommendation: If one bearing has failed, consider replacing both bearings on the same axle (both fronts or both rears).
Reasoning:
•Bearings wear at similar rates
•If one failed, the other is likely close to failure
•Replacing both prevents a second repair visit soon after
•Labor savings (vehicle is already disassembled)
When to Replace Only One:
•Vehicle has low mileage (under 75,000 miles)
•Budget constraints require staged repairs
•Only one bearing shows symptoms and the other tests perfect
At Speedway Tire and Service, we provide honest recommendations based on your vehicle's condition and your budget, never pushing unnecessary repairs.
Preventing Premature Wheel Bearing Failure
While wheel bearings are wear items that eventually fail, you can maximize their lifespan through proper care and driving habits.
Driving Habits
Avoid Potholes: Downtown LA's potholes are notorious bearing killers. Slow down and avoid potholes when possible. If unavoidable, slow down significantly before impact.
Reduce Curb Strikes: Hitting curbs damages bearings immediately or creates cracks leading to failure. Be careful when parallel parking and navigating tight spaces.
Gentle Turns: Aggressive cornering at high speeds loads bearings excessively. Moderate your speed through turns.
Proper Loading: Don't exceed your vehicle's weight capacity. Overloading accelerates bearing wear.
Smooth Driving: Aggressive acceleration, hard braking, and rough driving increase bearing stress.
Maintenance Practices
Regular Inspections: Have your suspension system inspected during routine maintenance. Early detection of bearing wear prevents catastrophic failure.
Tire Maintenance: Maintain proper tire pressure and rotate tires regularly. Uneven tire wear can indicate bearing problems, and proper tire maintenance reduces bearing stress.
Brake Maintenance: Keep your brakes in good condition. Dragging brakes generate excessive heat that damages bearings.
Seal Inspection: During brake service, have technicians inspect bearing seals for damage. Replacing damaged seals before water intrusion occurs prevents bearing failure.
Proper Wheel Installation: Ensure lug nuts are properly torqued during tire changes. Loose wheels damage bearings; over-tightened lug nuts can warp rotors and stress bearings.
Warning Sign Response
Don't Ignore Noise: When you first notice humming or grinding, schedule an inspection immediately. Early bearing wear is much less expensive to repair than catastrophic failure.
Stop Driving with Wobble: If you experience wheel wobble, stop driving and seek immediate repair or towing. Continued driving risks complete failure and accidents.
Address ABS Lights: ABS warning lights often indicate bearing problems. Have them diagnosed promptly.
When to Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to seek professional help prevents dangerous situations and expensive secondary damage.
Immediate Professional Attention Required
Grinding Noise: Loud grinding indicates advanced bearing failure. Drive directly to a repair shop or have the vehicle towed.
Wheel Wobble: Any noticeable wheel play or wobble requires immediate attention. Do not drive except to reach a repair facility.
Clicking with Play: Clicking noises combined with wheel play indicate imminent failure. Stop driving immediately.
ABS Warning Light with Noise: Combined ABS lights and bearing noise indicate the bearing has failed enough to affect the ABS sensor. Seek immediate repair.
Steering Wheel Vibration: Severe steering wheel shaking, especially at highway speeds, indicates dangerous bearing wear.
Schedule Inspection Soon
Humming Noise: Persistent humming that increases with speed indicates early to moderate bearing wear. Schedule an inspection within a week.
Noise Changes with Turns: Noise that changes during turns confirms bearing wear. Schedule an inspection soon.
Uneven Tire Wear: Unusual tire wear patterns can indicate bearing problems. Have it inspected during your next service.
Recent Impact: If you hit a major pothole or curb hard, have bearings inspected even without immediate symptoms. Damage may not be immediately apparent.
Why Choose Speedway Tire and Service for Wheel Bearing Repair
When you need wheel bearing diagnosis and repair in Downtown LA, Silver Lake, or Echo Park, Speedway Tire and Service provides the expertise, equipment, and honest service you deserve.
Our Advantages
25+ Years of Experience: We've diagnosed and repaired thousands of wheel bearing issues across all makes and models. Our technicians recognize bearing problems immediately and know the quirks of different vehicle types.
Professional Diagnostic Equipment: We use professional scan tools, torque wrenches, and specialized tools ensuring accurate diagnosis and proper installation.
Honest Assessments: We never push unnecessary repairs. If only one bearing needs replacement, we'll tell you. If both should be replaced for safety and value, we'll explain why.
Quality Parts: We use quality hub assemblies from trusted manufacturers (Timken, SKF, Moog, OEM) ensuring reliable, long-lasting repairs.
Proper Installation: Our technicians follow manufacturer torque specifications, protect seals during installation, and verify ABS sensor function after replacement.
Comprehensive Inspection: We inspect related components (suspension, brakes, tires) identifying any damage caused by bearing failure or contributing to the problem.
Fast Service: We understand your time is valuable. Our "in and out" service philosophy means we work efficiently to get you back on the road quickly without compromising quality.
Convenient Location: Located at 1165 West Sunset Blvd between Echo Park, Silver Lake, and Downtown LA, we're easy to reach from anywhere in central Los Angeles.
Fair Pricing: We provide competitive pricing with transparent estimates. No hidden fees, no surprise charges.
Warranty: Our repairs are backed by warranties on parts and labor, giving you peace of mind.
Our Service Area
We proudly serve drivers throughout central Los Angeles including:
•Downtown LA (DTLA)
•Silver Lake
•Echo Park
•Los Feliz
•Glendale
•Atwater Village
•Highland Park
•Boyle Heights
Whether you're a daily commuter navigating LA traffic or a weekend driver exploring the city, we're here to keep your vehicle safe and reliable.
Take Action: Don't Ignore Wheel Bearing Noise
Wheel bearing noise is your vehicle's warning that critical components are failing. Whether you're hearing humming, grinding, or growling, or experiencing wheel wobble or ABS warning lights, prompt professional diagnosis and repair prevents dangerous failures, expensive secondary damage, and potential accidents.
At Speedway Tire and Service, we've been providing honest, reliable auto repair in Downtown LA, Silver Lake, and Echo Park for over 25 years. Our experienced technicians use professional equipment to accurately diagnose wheel bearing problems and perform quality repairs that last.
Experiencing wheel bearing noise or symptoms?
Call us today at (213) 250-4254
We'll schedule a diagnostic inspection, identify the problem, provide a transparent estimate, and get your vehicle repaired quickly and correctly. Don't wait until a minor bearing problem becomes a dangerous failure—let Speedway Tire and Service restore your vehicle's safety and reliability.
Visit us at:Speedway Tire and Service1165 West Sunset BlvdLos Angeles, CA 90012
Hours:Monday-Friday: 8:00 AM - 6:00 PMSaturday: 8:00 AM - 5:00 PM Sunday: Closed
We're conveniently located between Echo Park, Silver Lake, and Downtown LA, just minutes from Glendale. Stop by for fast, honest service from LA's trusted auto repair experts.
About Speedway Tire and Service
Speedway Tire and Service has been providing honest, reliable auto repair to Los Angeles drivers for over 25 years. Located at 1165 West Sunset Blvd, we serve Downtown LA, Silver Lake, Echo Park, and surrounding communities with comprehensive automotive services including tire services, brake repair, suspension repair, wheel alignment, oil changes, engine diagnostics, and more.
Our "in and out" service philosophy means we respect your time, working efficiently to get you back on the road without compromising quality. We repair all makes and models using the latest diagnostic technology and quality parts. Visit our services page to learn more about how we can help keep your vehicle safe and reliable.
Contact Information:
•Phone: (213) 250-4254
•Address: 1165 West Sunset Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90012
•Website: https://speedwaytireandservice.com
Looking for an honest Auto Repair Shop in Los Angeles? Call Speedway Tire and Service Today
Whether you’re driving through LA traffic or cruising the freeways, your car deserves expert care. Located in Los Angeles, Speedway Tire and Service offers reliable oil changes, brake repairs, tire services, and more—all backed by experienced technicians and honest pricing.